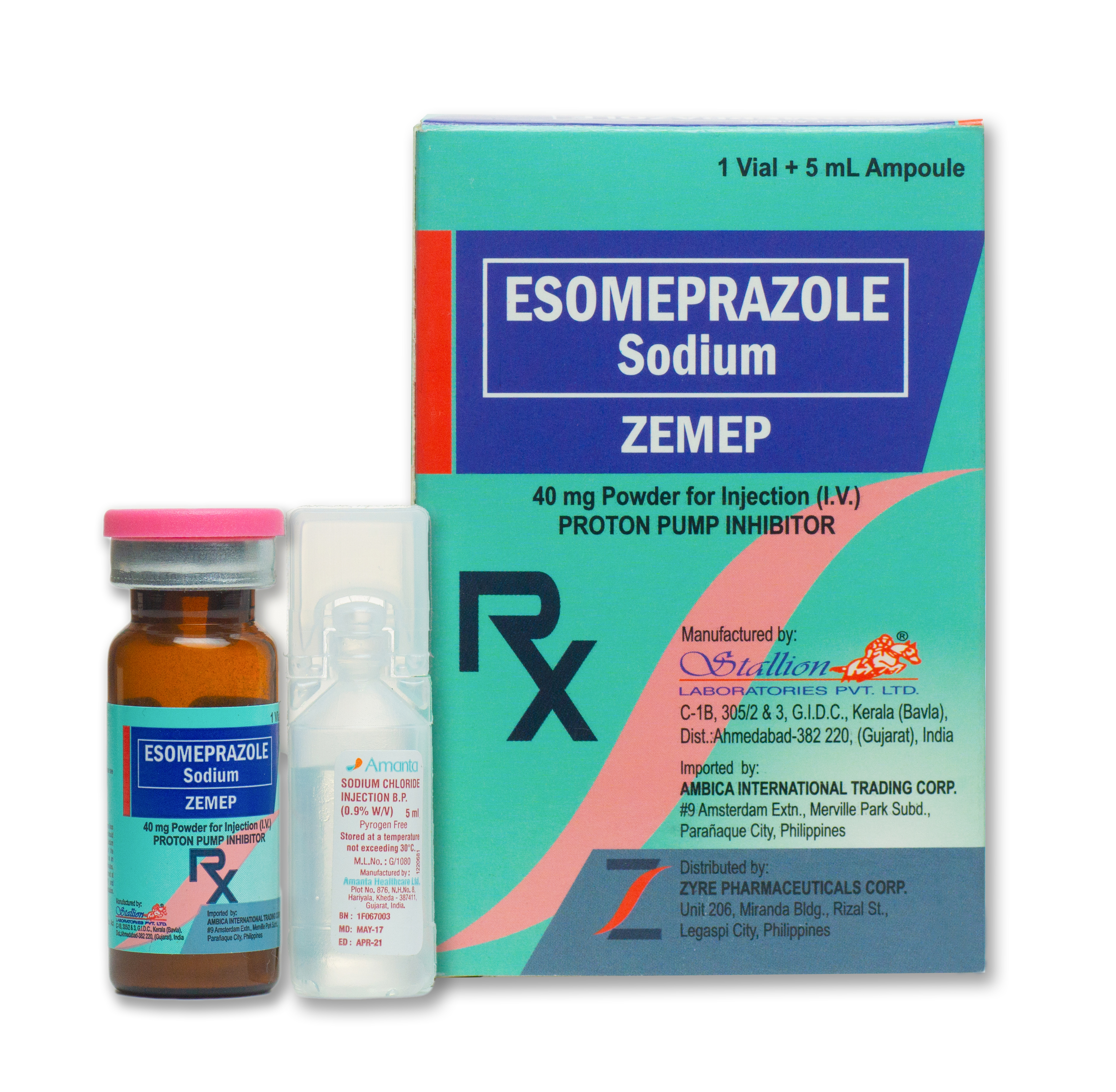
ZEMEP
Pharmacologic Classification
Esomeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor that suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+-ATPase in the gastric parietal cell. By acting specifically on the proton pump, Esomeprazole blocks the final step in acid production, thus reducing gastric acidity.
Therapeutic Indication
For the treatment of peptic ulcer disease and NSAID-associated ulceration, in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
For the treatment of acid-reflux disorders (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, H. pylori eradication, and prevention of gastroinetestinal bleeds with NSAID use.
It is indicated for prophylactic use.
Dosage Forms
40 mg vial + 5 ml diluent
Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics
Distribution. The plasma protein binding of esomeprazole is approximately 97%.
Metabolism. Mainly hepatic. Esomeprazole is completely metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system via CYP2C19 and CYP3A4. Metabolism produces inactive hydroxy and desmethyl metabolites, which have no effect on gastric acid secretion. Less than 1% of the parent drug is excreted in urine.
Excretion. Approximately 80% of the administered dose of esomeprazole is excreted as metabolites in urine and the remaining 20% is excreted in feces.
Dose Range
GERD with a history of Erosive Esophagitis. The recommended adult dose is either 20 or 40 mg Esomeprazole given once daily by intravenous injection (no less than 3 minutes) or intravenous infusion (10 to 30 minutes). Esomeprazole IV for injection should not be administered concomitantly with any other medications through the same intravenous site and or tubing. For healing of gastric ulcers associated with NSAID therapy the usual dose is 20 mg once daily. For prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers associated with NSAID therapy, patients at risk should be treated with 20 mg once daily.
Known Adverse Effects and Toxicities
Adverse effects: Blurred vision, confusion, drowsiness, dry mouth, flushing headache, nausea, rapid heartbeat, sweating
Special Precautions
Precautions: Increased risk of GI infections (eg Salmonella & Campylobacter) and fracture. Concomitant use with atazanavir , Vit B12, drugs metabolized by CYP2C19 & clopidogrel. Monitor mg levels before therapy & periodically, thereafter or for prolonged use. Discontinue therapy for at least days before chromagranin A measurements. Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to substituted benzimidazoles. Ijn: Concomitant use with nelfinavir.
Drug Interactions: Decreased absorption with ketoconazole, itraconazole & erlotinib. May increase absorption of digoxin. Concomitant use with esomeprazole & atazanavir; warfarin or other coumarin derivatives is not recommended. Increased plasma concentration with drugs metabolized by CYP2C19 eg diazepam, citalopram, imipramine, clomipramine, phenytoin.
Indication
Esomeprazole injection is indicated for the short-term treatment (up to 10 days) of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) patients with a history of erosive esophagitis as an alternative to oral therapy in patients when therapy with Esomeprazole Delayed-Release capsule is not possible or appropriate. For the treatment of peptic ulcer disease and NSAID – associated ulceration in gastroesophageal reflux disease and the Zollinger Ellison Syndrome.
Dosage And Administration
GERD with a history of Erosive Esophagitis. The recommended adult dose is either 20 or 40 mg Esomeprazole given once daily by IV injection (no less than 3 minutes) or IV infusion (10 to 30 minutes). Esomeprazole IV for injection should not be administered concomitantly with any other medications through the same IV site and or tubing. The IV line should always be flushed with either 0.9% NaCl injection, Lactated Ringer’s Injection, 5% Dextrose Injection , both prior to and after administration of Esomeprazole IV for injection. Safety and efficacy of Esomeprazole IV for injection as a treatment of GERD patients with a history or erosive esophagitis for more than 10 days have not been demonstrated. For healing of gastric ulcers associated with NSAIDs therapy the usual dose is 20 mg once daily. For prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers associated with NSAID therapy, patients at risk should be treated with 20 mg once daily.
Contraindications
Esomeprazole is rapidly absorbed after oral doses, with peak plasma levels occurring after about 1 to 2 hours. It is acid labile and an enteric-coated formulation has been developed. Bioavailability of esomeprazole increases with both dose and repeated administration to about 68 and 89% for doses of 20 to 40 mg respectively. Food delays and decreases the absorption of esomeprazole, but this does not significantly change its effect of intragastric acidity. Esomeprazole is about 97% bound to plasma proteins. The plasma elimination half-life is about 1.3 hours.
Pregnancy
There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Nursing Mothers: A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety and efficacy were observed between the elderly and younger individuals, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Adverse Reaction
Headache, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting and injection site reaction.
Direction For Reconstitution
Intravenous injection (20 or 40 mg) over no less than 3 minutes. The freeze-dried powder should be reconstituted with 5 ml of 0.9% NaCl injection, withdraw 5 ml of the reconstituted solution and administer as an intravenous injection over no less than 3 minutes. The reconstituted solution should be stored at room temperature up to 30˚ C (86˚ F) and administered within 12 hours after reconstituted. No refrigeration is required.
Availability
10 ml USP type I amber tubular vial + (diluents) 5 ml sodium chloride
Check out our available products
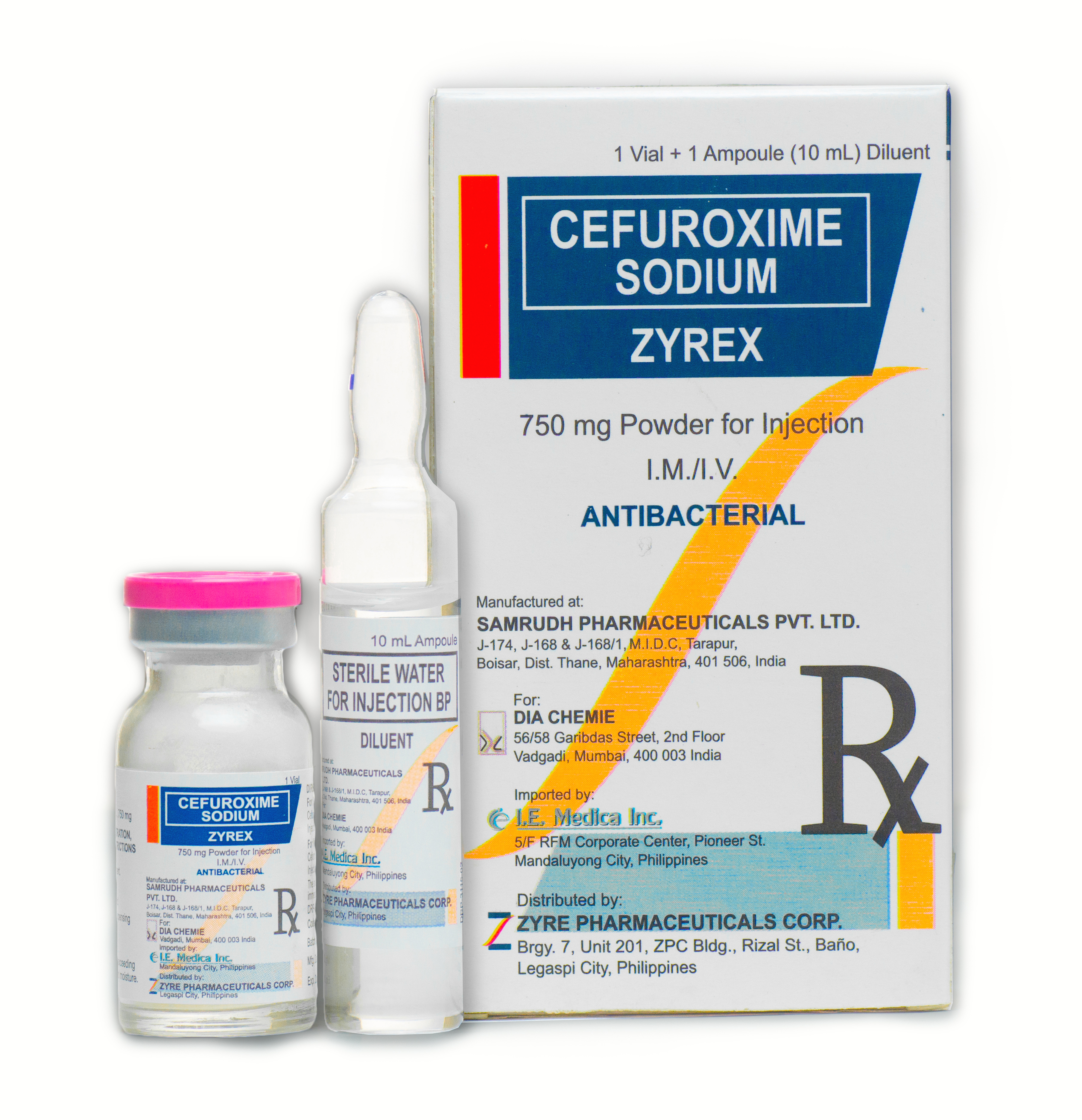
ZYREX
Cefuroxime is a semi-synthetic, broad-spectrum, second generation cephalosporins antibiotic forparenteral administration. Solutions of cefuroxime range in color from light yellow to amber, depending on the concentration and diluents used. The pH of...

NIRMIN 5-S
Description Dosage Strength & Form Pharmacodynamic Pharmacokinetic Indications Dosage and Administration Recommended Dosage Contraindications Warning and Precautions Drug Interactions Overdose Storage Presentation Description Descripton Nirmin is a clear,colorless injection containing well-balanced mixture...
Get In Touch
For questions, inquiry or to know more about our products, please feel free to call us at +63 052 742-2844 / +63 02 829-0181, email us at zyrepharma@yahoo.com or click the button below.
Contact Us